Sneaky2FA has emerged as one of the most sophisticated phishing-as-a-service platforms operating today. Known for targeting Microsoft 365 accounts with attacker-in-the-middle techniques, it has now expanded its toolkit with browser-in-the-browser capabilities designed to deceive even the most cautious users. This evolution marks a notable escalation in the broader phishing landscape and underscores how quickly threat actors continue to refine their tradecraft.
The integration of Browser-in-the-Browser, commonly referred to as BitB, allows Sneaky2FA to produce pop-ups that perfectly mimic legitimate Microsoft login windows. With this development, the platform has significantly strengthened its ability to steal credentials and seize active user sessions, even when two-factor authentication is enabled. As a result, organizations and individuals relying on Microsoft 365 face renewed pressure to stay vigilant and update their defensive strategies.
How Sneaky2FA Became a Leading Phishing-as-a-Service Platform
Sneaky2FA is part of a growing ecosystem of commercialized phishing tools that provide turnkey kits to cybercriminals. Alongside competitors such as Tycoon2FA and Mamba2FA, it has built a reputation for reliably compromising Microsoft 365 environments. Its earlier operations leaned heavily on SVG-based attacks and attacker-in-the-middle (AitM) methods.
These tactics work by proxying the victim’s entire authentication session, enabling attackers to intercept valid credentials and session tokens through counterfeit login portals. Sneaky2FA’s phishing pages relay authentication data to legitimate services in real time, providing threat actors with immediate access that bypasses standard protection layers. With the new BitB feature, this platform now presents an even more convincing façade to users.
New Browser-in-the-Browser Capabilities Push Deception Further
How Sneaky2FA Uses BitB
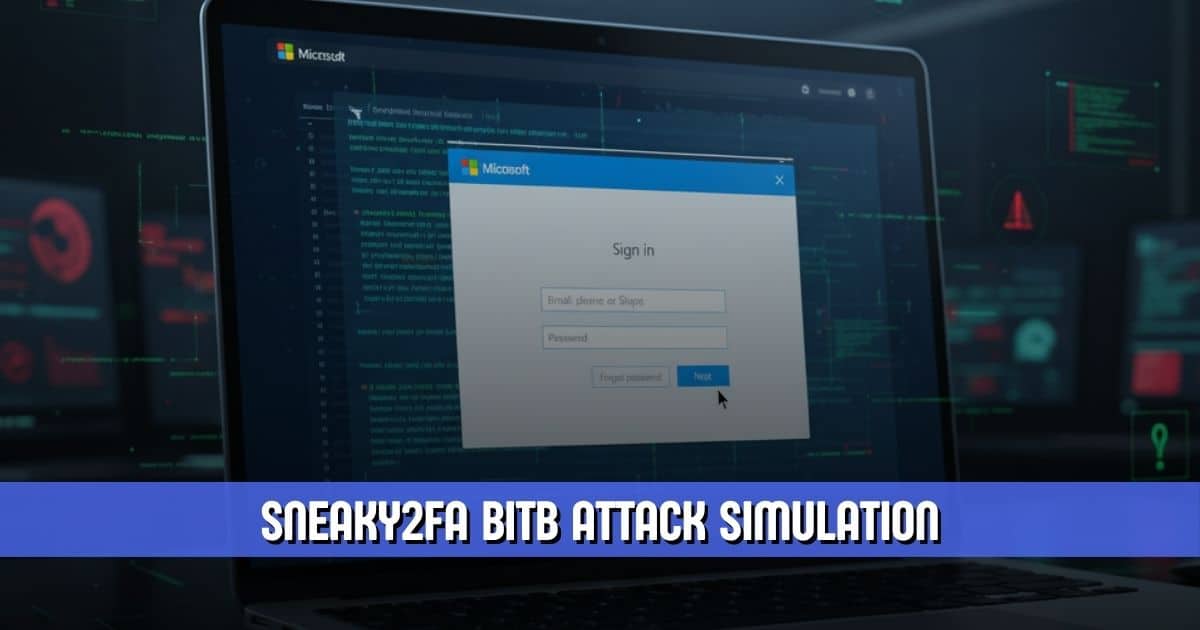
The latest report from Push Security details how the updated Sneaky2FA kit now deploys a BitB pop-up that convincingly imitates the Microsoft login experience. When victims click a “Sign in with Microsoft” button on a phishing site, a fake browser window appears. It’s a window that adjusts itself based on the user’s operating system and browser.
This dynamic presentation marks a shift toward hyper-realistic deception. Because the fake window displays a forged URL bar that looks identical to the real Microsoft domain configuration, users are more likely to trust what they see. The technique draws from research published in 2022 by security expert mr.d0x and has since been weaponized in attacks targeting platforms such as Facebook and Steam. With its adoption into, BitB is now a central component of modern phishing campaigns targeting corporate environments.
Sneaky2FA and Its Use of Real Microsoft Login Flows
Behind the cosmetic layer of the Browser-in-the-Browser trick, it still uses the attacker-in-the-middle method it was originally known for. Inside the fake BitB pop-up, the platform loads its reverse-proxy Microsoft phishing page, enabling it to capture both credentials and active session tokens.
By combining BitB with AitM, Sneaky2FA can authenticate directly into the victim’s account without alerting the user or triggering standard two-factor prompts. The integration of these techniques creates a seamless simulation of the legitimate login process. Nothing appears out of place until it is too late.
Conditional Loading and Obfuscation Help Sneaky2FA Evade Detection
Obfuscation at the Core
One of the defining characteristics of Sneaky2FA is its emphasis on stealth. Push Security’s analysis highlights that the platform’s phishing pages are crafted to avoid detection by researchers and automated tools.
The HTML and JavaScript code is heavily obfuscated. UI text is broken apart by invisible tags, interface elements are encoded as images instead of readable text, and background assets are embedded in ways that frustrate basic pattern-matching. This strategy significantly reduces the likelihood that security scanners will flag a Sneaky2FA page.
Conditional Loading to Hide from Analysts
To further complicate analysis, Sneaky2FA uses conditional loading to redirect automated scanners, bots, or suspected researchers to benign websites. Real victims, however, see the full phishing flow, from Cloudflare Turnstile verification to the fabricated Microsoft login prompt.
How Users Can Detect a BitB Attack
Browser-in-the-Browser attacks rely heavily on visual deception, but there are still ways for users to identify them. A genuine browser pop-up behaves as a standalone application window. It can be dragged outside the boundaries of the parent browser and appears as a separate instance in the taskbar.
By contrast, a BitB pop-up is confined to the parent page because it exists within an iframe. Attempting to move it beyond the browser window will reveal that it cannot detach. This simple test can immediately alert users to a fraudulent login attempt. Awareness and education are essential, especially as tools like Sneaky2FA continue to adopt more convincing methods.
Sneaky2FA and the Broader PhaaS Landscape
Sneaky2FA is not acting alone in adopting BitB capabilities. Another phishing-as-a-service platform, Raccoon0365 (also known as Storm-2246), introduced similar features before being disrupted by Microsoft and Cloudflare. That operation had stolen thousands of Microsoft 365 credentials before being shut down, underscoring the scale of damage such services can inflict.
As law enforcement and security companies continue to dismantle these platforms, new variants emerge with more advanced capabilities. Sneaky2FA’s recent update demonstrates how quickly threat actors can adapt and expand their methods.
Why Sneaky2FA’s Advancements Matter for Organizations
With the addition of Browser-in-the-Browser, Sneaky2FA has become significantly more dangerous for businesses relying on Microsoft 365. Many organizations depend heavily on two-factor authentication to secure their accounts, but Sneaky2FA’s AitM techniques allow attackers to bypass these safeguards entirely.
Because the attacks blend real login flows with forged interfaces, users have fewer visual cues to indicate something is wrong. The impersonation is precise, the deception is multilayered, and the outcome is immediate access for attackers. Organizations must plan for the reality that credential theft may occur even when authentication procedures are followed correctly.
Strengthening Defenses Against Sneaky2FA
To reduce exposure to campaigns involving Sneaky2FA, security teams should implement conditional access policies, adopt phishing-resistant authentication methods such as hardware security keys, and continuously educate users about tactics like BitB. Threat detection tools must also be updated to account for obfuscation patterns and AitM signatures associated with modern phishing kits.
While no single measure can fully eliminate the risk posed by Sneaky2FA, layered security, stronger authentication practices, and user awareness remain the most effective countermeasures.
Conclusion
Sneaky2FA continues its rapid ascent as one of the most sophisticated phishing-as-a-service kits on the market. Its new Browser-in-the-Browser capabilities represent a significant escalation in deceptive tactics targeting Microsoft 365 users. By blending visual mimicry with attacker-in-the-middle techniques, Sneaky2FA provides criminals with a powerful means of seizing credentials and session tokens.
As phishing tools grow more realistic and evasive, organizations must adopt stronger defenses and keep pace with evolving threats. Understanding how platforms like Sneaky2FA operate is a critical step toward preventing account takeover and safeguarding sensitive data.